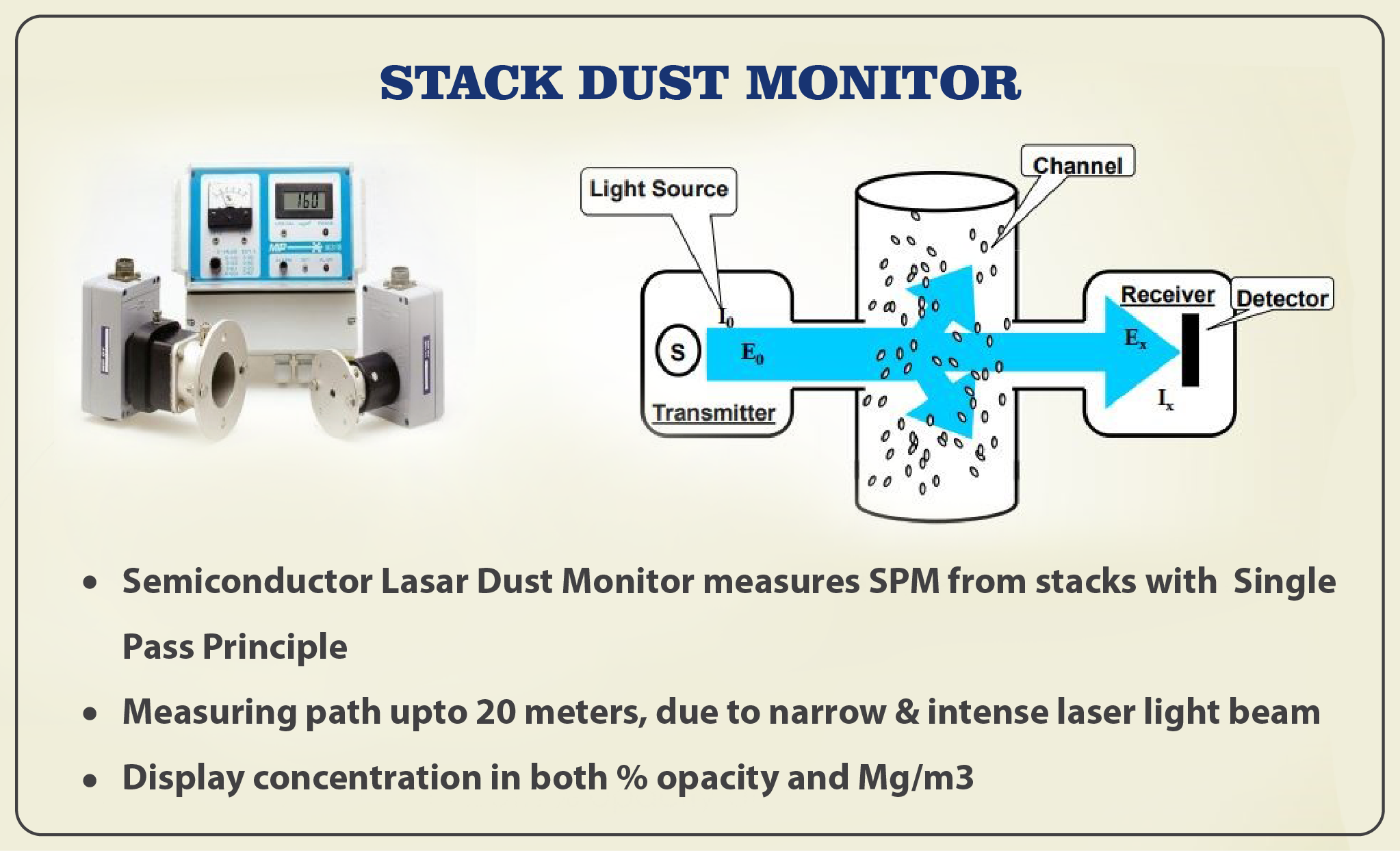
VOC Monitoring System In Andhra Pradesh
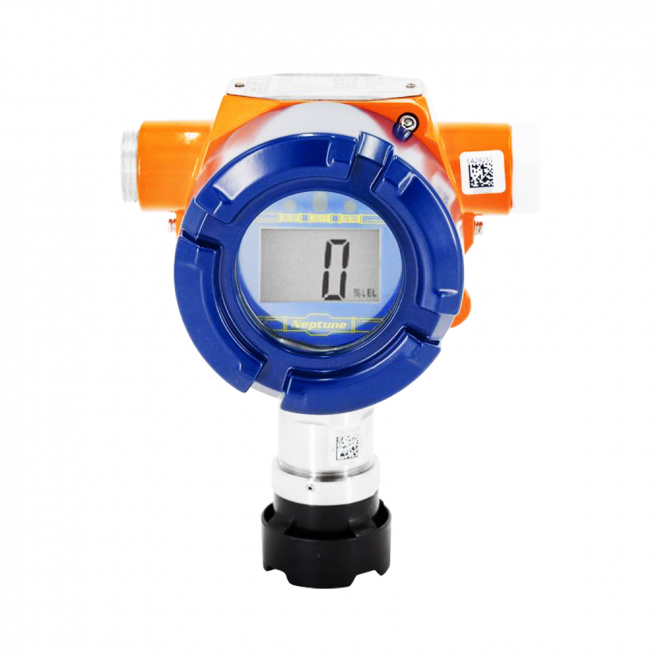
A VOC sensor informed ventilation system can optimize indoor air quality while minimizing energy use. There are over 5,000 VOCs that are expelled by breathing, cooking, bodily functions, perfumes, deodorants, paint, cleaners, cigarettes, office supplies, etc. VOC sensor monitors these gases and provides a CO2 equivalent ppm (parts per million) output which is then input to a DCV system.
The VOC sensor eliminates the need for frequent manual calibration by providing a relative measurement and using an Automatic Baseline Correction (ABC) logic algorithm. With ABC self-correction, the sensor constantly adjusts the 450 ppm baseline (outside air) to eliminate any sensor drift. The logic drives the sensor to quickly reduce the baseline when a time of low measurement is sensed.
The VOC sensors directly measures ambient concentrations of a broad range of reducing gases associated with bad air quality. Examples are alcohols, aldehydes, ketones, organic acids, amines, organic chloramines, aliphatic and aromatic hyrocarbons. These gases all burn and cause the VOC sensor ppm output to increase. Opposite examples are sulphuric acid, nitric acid and ozone. These three are oxidizing gases and will not cause the VOC sensor ppm output to increase.